논문 자세히 보기
-
구강 유래 유산균(Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum)의 혈당 강하 효과
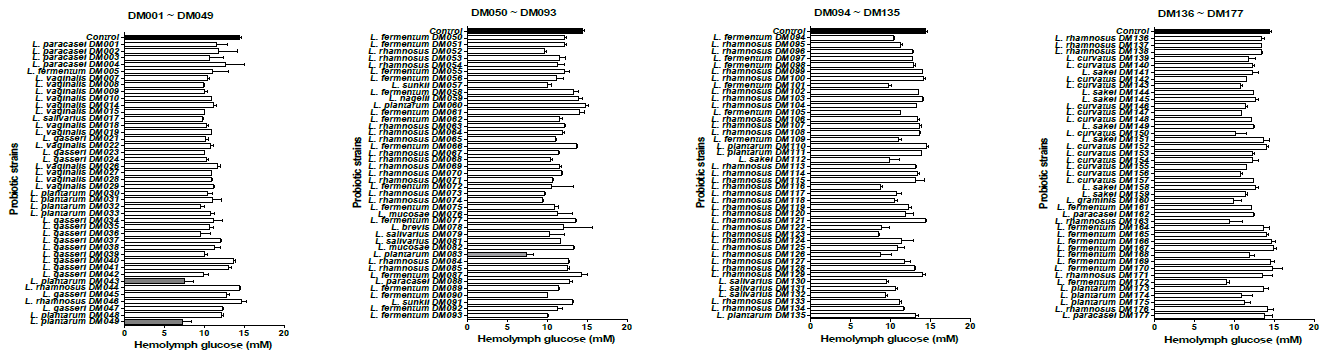
 닥스메디오랄바이옴은 한국인에게서 채취한 구강 유래물에 포함된 168종의 유산균주 중 혈당 강하 효과를 지닌 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083(Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum DM083)을 찾아냈습니다. 기존 연구의 기술적 한계를 극복하기 위한 대안으로 초파리 모델을 활용해 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083이 혈당 강하 효능을 발휘하는 것을 밝혀냈습니다. 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083은 초파리의 장에서 특정 장호르몬 분비를 촉진 시키고, 이후 인슐린 분비 세포로 이동해서 인슐린 유전자 발현을 증가시킴으로써 혈당 강하 효능을 발휘할 수 있었습니다. 또한 초파리의 인슐린 및 당 대사 과정은 마우스와 거의 유사하기 때문에, 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083의 혈당 강하 효능이 마우스 및 사람에서도 충분히 발휘될 수 있을 것이라고 밝혔습니다.The Beneficial Effect of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum DM083 on Restoring the Hyperglycemia in High-Sucrose Diet-Fed Drosophila, 2024 February 16
닥스메디오랄바이옴은 한국인에게서 채취한 구강 유래물에 포함된 168종의 유산균주 중 혈당 강하 효과를 지닌 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083(Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum DM083)을 찾아냈습니다. 기존 연구의 기술적 한계를 극복하기 위한 대안으로 초파리 모델을 활용해 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083이 혈당 강하 효능을 발휘하는 것을 밝혀냈습니다. 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083은 초파리의 장에서 특정 장호르몬 분비를 촉진 시키고, 이후 인슐린 분비 세포로 이동해서 인슐린 유전자 발현을 증가시킴으로써 혈당 강하 효능을 발휘할 수 있었습니다. 또한 초파리의 인슐린 및 당 대사 과정은 마우스와 거의 유사하기 때문에, 락티플란티바실러스 플란타룸 DM083의 혈당 강하 효능이 마우스 및 사람에서도 충분히 발휘될 수 있을 것이라고 밝혔습니다.The Beneficial Effect of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum DM083 on Restoring the Hyperglycemia in High-Sucrose Diet-Fed Drosophila, 2024 February 16 -
충치균 생장을 억제하는 구강 유래 유산균 리모시락토바실러스 퍼멘텀 (Limosilactobacillus fermentum)
스트렙토코커스 뮤탄스 (Streptococcus mutans) 는 대표적인 충치균으로서 유아 또는 노년들의 치아 우식을 유발하는 입 속 유해균입니다.
닥스메디 오랄바이옴 연구소에서는 스트렙토코커스 뮤탄스 생장을 억제하는 유산균인
리모시락토바실러스 퍼멘텀 (Limosilactobacillus fermentum) 을 건강한 성인의 구강으로부터 분리 성공했습니다.
이와 더불어 닥스메디 오랄바이옴 연구소는 치아교정용 철사, 인공치아(hydroxyapatite), 및 실제치아 샘플을 이용해서
스트렙토코커스 뮤탄스 (Streptococcus mutans) 가 유발하는 충치 플라그 형성이 리모시락토바실러스 퍼멘텀
(Limosilactobacillus fermentum) 에 의해 효과적으로 억제되는 것을 확인하였습니다.
세계 최초로 실제 치아 샘플을 이용해서 유산균의 충치 플라그 형성 억제 효능을 증명하였고, 이러한 결과는
네이처 출판 그룹에서 출간하는 온라인 과학 잡지 (Scientific Reports)에 실렸습니다.
•Antimicrobial activity of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains isolated from the human oral cavity against Streptococcus mutans 네이처 출판 그룹 (Scientific Reports), 2023 May 17 -
새로운 유산균(Lactobacillus reuteri AN417)의 항균 효능 검증 논문 출간
Lactobacillus reuteri AN417은 닥스메디, 사과나무치과의생명연구소(ATIBS)가 한국생명공학연구원(KRIBB)과 공동연구를 통해 항균, 항염 특성을 규명한 새로운 프로바이오틱스 유산균이다.

AN417 균주 배양액을 이용해 대표적인 구강의 병원성 박테리아(Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Streptococcus mutans)에 대한 항균력을 검증한 결과, 최소저해부피(minimal inhibitory volume, MIV) 수치는 10, 20, 30%로 각각 밝혀졌다. 이는 AN417이 치주염을 비롯한 구강 질환을 유발하는 대표적인 세균을 억제하는 탁월한 효과가 있음을 의미한다. 특히 치매를 비롯한 전신 질환에 깊게 연관되어 있는 P. gingivalis에 대한 항균력이 뛰어난 것으로 나타나, 향후 구강뿐만 아니라 전신 질환의 치료에도 적용할 수 있는 확장성과 가능성을 보여주고 있다.
ATIBS와 닥스메디는 지난 2020년 11월 2일 쎌바이오텍과 AN417 균주을 이용한 기능성 식품 개발을 위한 MOU를 맺었다. 이번 논문 출간을 계기로 닥스메디는 AN417을 적용한 구강 제품 개발을 시도하고 있으며, 쎌바이오텍과의 공동연구를 강화하는 한편 후속 연구와 새로운 제품 개발에 박차를 가하고 있다.
-
미생물 생물전환 기술을 활용하여 생산한 불포화지방산의 유방암세포에 대한 항암효과 규명 논문 게재 확정
미생물 생물전환 기술을 활용하여 생산한 불포화지방산인 ω-hydroxyundec-9-enoic acid (ω-HUA)는 AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) 활성화를 통해 유방암 세포의 사멸(apoptosis)을 유도하였다.
AMPK의 활성화에 의해서 암세포는 mitochondrial membranepotential 저하뿐만 아니라 활성 산소(reactive oxygenspecies; ROS)를 생산함으로써 사멸 유도를 가속화 시킨다는 사실을 규명하였다.
분자생물학적인 생산물로써 AMPK 인산화 수준, cleaved caspase-3, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) 단백질의 발현 수준을 확인하였고, Bcl-2와 같은 항세포사멸(anti-apoptotic) 인자의 감소와 친세포사멸(pro-apoptotic) 인자인 Bax의 발현을 확인하였다.
또한, ω-HUA 스트레스하에 ROS scavenger인N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)의 처치에 의해서 AMPK의 불활성화, 세포사멸(apoptosis)의 감소 등으로 암세포가 회복되는 현상을 관찰하였다.
이는 ω-HUA가 유방암 세포의 미토콘드리아 활성산소(mitochondrial ROS)를 생성하고 AMPK의 활성화를 통해 암세포의 사멸을 유도한다는 것을 의미하며, 유방암 세포에서 AMPK를 타깃으로 하는 항암제(anticancer agent)로도 활용이 가능함을 의미하는 것이다.
-
 비피도박테리움(Bifidobacterium) 프로바이오틱스에 의한 비소세포 폐암의 항암효과에 대한 논문 게재 확정비피도박테리움(Bifidobacterium) 프로바이오틱스에 의한 비소세포폐암 세포의 항암 효과에 대한 연구 결과가 "Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (JMB)" 국제학술지에 게재승인되었습니다.연구내용:비소 세포 폐암 (NSCLC)에 대한 화학 요법 요법은 인체에 다양한 악영향을 미칩니다. 이러한 이유로, 프로바이오틱스는 암 예방을 위한 안전하고 자연적인 보완 전략으로서의 잠재적 가치에 대해 주목을 받았습니다. 이 연구는 비소세포성폐암(non–small cell lung cancer; NSCLC) 세포주에서 생균 박테리아 비피도박테리움 비피덤(Bifidobacterium bifidum; BB), 비피도박 테리움 롱검 (Bifidobacterium longum; BL), 비피도박테리움 락티스 (Bifidobacterium lactis; BLA), 비피도박테리움 인판티스 1 (Bifidobacterium infantis; BI1) 및 비피도박테리움 인판티스 2 (BI2)의 물추출물의 항암 효과를 분석 하였습니다.프로 바이오 틱 비피 도박 테 리움 종의 물추출물이 NSCLC 세포주 A549, H1299 및 HCC827에 적용될 때, 세포 사멸이 상당히 증가 하였습니다. 특히, BB 및 BLA로부터의 물추출물은 세포 증식을 현저하게 감소시켰습니다. BB 물추출물에 의해 유도 된 p38 인산화는 cleaved caspase 3 및 cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)(PARP)의 발현을 증가시켜 결과적으로 A549 및 H1299 세포의 사멸을 유도하였습니다. p38 억제제 SB203580을 적용한 경우, p38의 인산화가 감소하고, cleaved caspase 3 및 cleaved PARP의 발현이 억제되어, 세포 사멸이 감소되었습니다. 또한, BB 물추출물은 MMP-9의 분비를 감소시켜 암 세포 침습을 억제 하였습니다. 대조적으로, short hairpin RNA shMMP-9 (MMP-9의 녹다운)를 암 세포로 형질 감염시킨 후, BB 물추출물 처리는 암 세포 침습성을 억제하지 못했습니다.우리의 결과에 따르면, 비피도박테리움 종으로 구성된 프로바이오틱스는 미래에 보조 항암 치료로 유용 할 수 있습니다.
비피도박테리움(Bifidobacterium) 프로바이오틱스에 의한 비소세포 폐암의 항암효과에 대한 논문 게재 확정비피도박테리움(Bifidobacterium) 프로바이오틱스에 의한 비소세포폐암 세포의 항암 효과에 대한 연구 결과가 "Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (JMB)" 국제학술지에 게재승인되었습니다.연구내용:비소 세포 폐암 (NSCLC)에 대한 화학 요법 요법은 인체에 다양한 악영향을 미칩니다. 이러한 이유로, 프로바이오틱스는 암 예방을 위한 안전하고 자연적인 보완 전략으로서의 잠재적 가치에 대해 주목을 받았습니다. 이 연구는 비소세포성폐암(non–small cell lung cancer; NSCLC) 세포주에서 생균 박테리아 비피도박테리움 비피덤(Bifidobacterium bifidum; BB), 비피도박 테리움 롱검 (Bifidobacterium longum; BL), 비피도박테리움 락티스 (Bifidobacterium lactis; BLA), 비피도박테리움 인판티스 1 (Bifidobacterium infantis; BI1) 및 비피도박테리움 인판티스 2 (BI2)의 물추출물의 항암 효과를 분석 하였습니다.프로 바이오 틱 비피 도박 테 리움 종의 물추출물이 NSCLC 세포주 A549, H1299 및 HCC827에 적용될 때, 세포 사멸이 상당히 증가 하였습니다. 특히, BB 및 BLA로부터의 물추출물은 세포 증식을 현저하게 감소시켰습니다. BB 물추출물에 의해 유도 된 p38 인산화는 cleaved caspase 3 및 cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)(PARP)의 발현을 증가시켜 결과적으로 A549 및 H1299 세포의 사멸을 유도하였습니다. p38 억제제 SB203580을 적용한 경우, p38의 인산화가 감소하고, cleaved caspase 3 및 cleaved PARP의 발현이 억제되어, 세포 사멸이 감소되었습니다. 또한, BB 물추출물은 MMP-9의 분비를 감소시켜 암 세포 침습을 억제 하였습니다. 대조적으로, short hairpin RNA shMMP-9 (MMP-9의 녹다운)를 암 세포로 형질 감염시킨 후, BB 물추출물 처리는 암 세포 침습성을 억제하지 못했습니다.우리의 결과에 따르면, 비피도박테리움 종으로 구성된 프로바이오틱스는 미래에 보조 항암 치료로 유용 할 수 있습니다. -
 SCI급 저널 ‘BMC Oral Health’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재
SCI급 저널 ‘BMC Oral Health’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소 연구진 김혜성 이사장과 김영연 병원장이 참여한 연구가 SCI급 저널인 ‘BMC Oral Health’에 등재되었습니다.

● 논문명
Implant survival and patient satisfaction in completely edentulous patients with immediate placement of implants: a retrospective study.
● 저자
Kim HS1, Cho HA2, Kim YY3, Shin H4.
1Departments of Oral Implantology, Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple Tree Dental Hospital, 1450, Jungang-ro, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10387, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Social and Humanity in Dentistry, Wonkwang University School of Dentistry, 460 Iksan Dearo, Iksan, North Jula, 54538, Republic of Korea.
3Departments of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple Tree Dental Hospital, 1450, Jungang-ro, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10387, Republic of Korea.
4Department of Social and Humanity in Dentistry, Wonkwang University School of Dentistry, 460 Iksan Dearo, Iksan, North Jula, 54538, Republic of Korea. shinhosung@gmail.com.● 논문요약
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
This study evaluated full-arch rehabilitation of patients with immediately placed implants in terms of the cumulative implant survival rate, risk factors for implant failure, and patient satisfaction.
METHODS:
Time-to-event data of 52 completely edentulous jaws (370 implants) were collected using retrospective clinical chart review for the time period from 2008 to 2014. A conventional two stage approach for surgery was adopted to immediately placed implants in the maxilla, and immediate placement and immediate loading protocols for the mandible were followed. The study calculated the 7-year cumulative survival rates (CSR), and a Bayesian hierarchical Cox proportional hazard model was used to measure the effect of covariates. Patient satisfaction on chewing ability, esthetic appearance, and overall satisfaction was also measured with a face-to-face interview survey.
RESULTS:
Of the total 370 implants, 194 were immediate placement. Two delayed loading maxillary implants failed within the first year, and another one failed in the second year of loading. Two failures were recorded in the first year and one in seven years for the immediate loading mandibular implants. The 1-, 5-, and 7-year CSR of the 370 implants were 0.989 (0.979, 1.000), 0.986 (0.975, 0.998), and 0.978 (0.957, 0.999), respectively. Only the length of the implant affected implant failure (p < 0.05); other patient characteristics, systemic diseases, implant diameter, immediate loading, and immediate placement, did not have an effect on implant failure rates. Patients reported a high degree of satisfaction regardless of their age group or length of the observation period.
CONCLUSIONS:
Immediately placed implant had CSR as high as delayed placed implants, and 7-year CSRs of immediate loading were not significantly different from delayed loading. The procedure also had a high degree of chewing ability, esthetic appearance, and overall satisfaction. The study results suggested that the clinical procedures applied in this study to completely edentulous patients were acceptable rehabilitation procedures.
원문 링크: https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-018-0669-1
관련기사 링크: http://www.mygoyang.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=49585
-
 SCI 저널 ‘Biological Trace Element Research’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재
SCI 저널 ‘Biological Trace Element Research’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소 연구진 김혜성 이사장과 배광학 연구소장이 공동으로 참여한 연구가 SCI 저널인 Biological Trace Element Research에 등재되었습니다.

● 논문명
Association of Periodontitis with the Concentration Levels of Germanium and Tin in Hair
● 저자
Hye-Sung Kim1 & Hyun-Jae Cho2,3 & Soo-Myoung Bae4 & Young-Youn Kim1 & Sung-In Baek1 & Kwang-Hak Bae1
1Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple tree Dental Hospital, Jungang-ro 1573, Goyang-si, Gyounggi-do, 10381, South Korea.
2Department of Preventive and Public Health Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea.
3Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea.
4Department of Dental Hygiene, College of Dentistry & Research Institute of Oral Science, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung-si, South Korea.
5Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple tree Dental Hospital, Jungang-ro 1573, Goyang-si, Gyounggi-do, 10381, South Korea.
● 논문요약
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether or not the concentration levels of certain kinds of trace elements in hair are associated with periodontitis.We studied a total of 109 participants, which are composed of 25 participants with periodontitis and 84 participants without periodontitis. Periodontal conditions were assessed by measuring the periodontal clinical attachment loss and pocket depth,which were determined at six sites of all teeth. Periodontitis was defined according to the criteria of periodontitis proposed by CDC-AAP. The hair sampleswere washed with acetone, water, and extran (1%v/v), and then aliquots of hair samples were wet-ashed. This sample solution was analyzed by Perkin-Elmer Mass Spectrometer. The odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals of the concentration levels of trace elements for periodontitis were calculated bymultivariate logistic regression analysis. After adjusting all confounders, it was found that the higher concentration level of germanium in hair was significantly and positively associated with periodontitis (odds ratio [OR] 7.12; 95% confidential interval [CI] 2.03–25.00). The higher concentration level of tin in hair was significantly and negatively associated with periodontitis (OR 0.27; 95% CI 0.08–0.94). It was concluded that there was a significant relationship between periodontitis and the concentration level of germanium and tin in hair
링크: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs12011-018-1296-z
-
 SCI 저널 ‘Acta Odontologica Scandinavica’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재
SCI 저널 ‘Acta Odontologica Scandinavica’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소 연구진 배광학 연구소장과 최형길 과장이 참여한 연구가 SCI 저널인 Acta Odontologica Scandinavica에 등재되었습니다.

● 논문명
Association between age at asthma diagnosis and tooth loss.
● 저자
Choi H1,2, Bae KH2, Lee JW1,3.
1a Department of Dental Services Management and Informatics , Seoul National University , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
2b Research Institute, Apple Tree Dental Hospital , Goyang-si , Korea.
3c Department of Preventive Dentistry and Public Oral Health , Oral Science Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Dentistry , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
● 논문요약
Abstract
OBJECTIVES:
This study aimed to investigate the association between age at asthma diagnosis and tooth loss due to caries using data obtained from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
A complex sample multivariable linear regression was used, and the results were analysed. Age at diagnosis and the number of teeth lost were set as independent and dependent variables, respectively. Among the total 65,973 subjects, 10,056 aged <12 years and 11,714 with missing values in dependent and independent variables were excluded. Asthmatic subjects were divided into the following age groups based on the age at diagnosis: 0-6 years, 7-12 years, 13-18 years, 19-28 years, and 29-64 years. In each analysis, the calibration was performed by adding covariates to each model.
RESULTS:
Compared with the no asthma group (β = 0), the values of β in asthmatic subjects belonging to the age groups 0-6 years (β = 0.794, 0.521, 0.560) and 7-12 years (β = 0.527, 0.407, 0.437) were high in all models.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings revealed significant increase in tooth loss due to caries after early asthma diagnosis at 0-6 years (β = 0.560, p < .001) and 7-12 years (β = 0.437, p < .001). Clinicians need to shift their perception of dental risks in young asthmatic patients and provide active oral health care to them.
링크: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00016357.2018.1436723
-
 SCI급 논문저널 Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCIE급 저널인 Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 게재됨.
SCI급 논문저널 Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCIE급 저널인 Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 게재됨. -
 SCIE급 저널 'PLoS ONE'에 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCI급 저널인 PLoS ONE에 2017년 10월 게재됨.
SCIE급 저널 'PLoS ONE'에 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCI급 저널인 PLoS ONE에 2017년 10월 게재됨. ● 논문명
● 논문명
Is yogurt intake associated with periodontitis due to calcium?
● 저자
Hye-Sung Kim¹, Young-Youn Kim¹, Jeong-Kyu Oh¹, Kwang-Hak Bae¹*
¹Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple tree Dental Hospital, Goyang-si, Gyounggi-do, Korea
*Corresponding author
● 논문요약
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to determine whether the lower intakes of yogurt, milk, and calcium are associated with periodontitis in a nationally representative sample of Korean adults.This study comprised 6,150 adults 19or more years old who took both periodontal examination and nutrition survey. The frequency of yogurt and milk intake was examined with a food frequency questionnaire. The amount of calcium intake was calculated with dietary intakes data gained from complete one-day 24-hour recall interviews. Periodontitis was assessed using the Community Periodontal Index (CPI). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed for the whole sample and subgroups with the strata of age, gender, or smoking, in a complex sampling design .Less intake of yogurt was significantly associated with periodontitis (oddsratio[OR]0.82, 95% confidential interval[CI]0.70-0.97), but neither less intake of milk (OR1.04, 95% CI 0.89-1.20)nor lower intake of calcium (OR1.04, 95% CI0.89-1.21) was significantly associated with periodontitis. In the subgroup analysis, no difference in the association of yogurt intake with periodontitis was found according to the strata of age, gender, and smoking. In conclusion, periodontitis was significantly associated with the less intake of yogurt among the Korean adults, but the calcium contained in yogurt is not likely to cause it. -
 SCI급 저널 'BIOLOGICAL TRACE ELEMENT RESEARCH'에 논문 게재
SCI급 저널 'BIOLOGICAL TRACE ELEMENT RESEARCH'에 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소 배광학 연구소장이 공동으로 참여한 연구가 SCI급 저널인 BIOLOGICAL TRACE ELEMENT RESEARCH에 2017년 8월에 등재되었습니다.

●논문명Association of Some Vitamins and Minerals with Periodontitis in a Nationally Representative Sample of Korean Young Adults.●저자● 논문요약The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the intakes of some kinds of vitamins and minerals are associated with periodontitis in a nationally representative sample of young adults. This study comprised 2049 young adults aged 19-39 years who took both periodontal examination and nutrition survey. The vitamin and mineral intakes were calculated from dietary intake data gained by complete one-day 24-h recall interviews, and the intake levels for each nutrient were classified by the Recommended Nutrient Intake (RNI) in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans and median values. Periodontitis was assessed using Community Periodontal Index (CPI). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed in a whole sample and subgroups with the strata of gender or smoking, following a complex sampling design. In analyses according to RNI, a lower intake of niacin was significantly associated with periodontitis in young adults (odd ratio [OR] 1.47, 95% confidential interval [CI] 1.09-2.00) and in its subgroup of women (OR 1.70; 95% CI 1.10-2.64) and current non-smokers (OR 1.75; 95% CI 1.22-2.51). Whereas, in analyses according to median intake values, there were significant associations of periodontitis with a lower intake of niacin in women (OR 1.58; 95% CI 1.02-2.46) and current non-smokers (OR 1.50; 95% CI 1.01-2.22), with lower intake of vitamin C in women (OR 1.66; 95% CI 1.04-2.64) and in current non-smokers (OR 1.49; 95% CI 1.04-2.14), with lower intake of iron in women (OR 1.85; 95% CI 1.11-3.07), and with lower intake of vitamin A marginally in women (OR 1.56; 95% CI 1.00-2.44). In young adults, periodonitis is significantly associated with the lower intakes of niacin, vitamin C, and iron, especially in women and current non-smokers.원문은 아래 링크에서 확인해 주세요! -
 SCI 저널 ‘Oral Diseases’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재
SCI 저널 ‘Oral Diseases’에 본원 연구진 논문 게재닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소 연구진 김혜성 이사장과 김영연 병원장이 참여한 연구가 SCI 저널인 Oral Diseases에 등재되었습니다.

● 논문명
Genetic alterations in mesiodens as revealed by targeted next-generation sequencing and gene co-occurrence network analysis
● 저자
Kim YY1, Hwang J2, Kim HS1, Kwon HJ1, Kim S3, Lee JH4, Lee JH5.
1Institute of Oral Science, Apple Tree Dental Hospital, Ilsansuh-gu, Goyang, Korea.
2Department of IT Convergence and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, Korea.
3Department of Life Science, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, Korea.
4Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Dongdaemoon-gu, Seoul, Korea.
5Department of Prosthodontics, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seodaemoon-gu, Seoul, Korea.
● 논문요약
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Mesiodens is the most common type of supernumerary tooth which includes a population prevalence of 0.15%-1.9%. Alongside evidence that the condition is heritable, mutations in single genes have been reported in few human supernumerary tooth cases. Gene sequencing methods in tradition way are time-consuming and labor-intensive, whereas next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics are cost-effective for large samples and target sizes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
We describe the application of a targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) and bioinformatics approach to samples from 17 mesiodens patients. Subjects were diagnosed on the basis of panoramic radiograph. A total of 101 candidate genes which were captured custom genes were sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq 2500. Multistep bioinformatics processing was performed including variant identification, base calling, and in silico analysis of putative disease-causing variants.
RESULTS:
Targeted capture identified 88 non-synonymous, rare, exonic variants involving 42 of the 101 candidate genes. Moreover, we investigated gene co-occurrence relationships between the genomic alterations and identified 88 significant relationships among 18 most recurrent driver alterations.
CONCLUSION:
Our search for co-occurring genetic alterations revealed that such alterations interact cooperatively to drive mesiodens. We discovered a gene co-occurrence network in mesiodens patients with functionally enriched gene groups in the sonic hedgehog (SHH), bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP), and wingless integrated (WNT) signaling pathways.
링크: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/odi.12680
-
 SCI급 저널 'PLoS ONE'에 논문 게재 예정닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCI급 저널인 PLoS ONE에 accept 되어, 게재될 예정 (in press) 입니다.
SCI급 저널 'PLoS ONE'에 논문 게재 예정닥스메디의 연구협력 기관인 사과나무치과병원 구강과학연구소에서 연구하고 발표한 논문이 SCI급 저널인 PLoS ONE에 accept 되어, 게재될 예정 (in press) 입니다. ● 논문명Is yogurt intake associated with periodontitis due to calcium?● 저자Hye-Sung Kim¹, Young-Youn Kim¹, Jeong-Kyu Oh¹, Kwang-Hak Bae¹*
● 논문명Is yogurt intake associated with periodontitis due to calcium?● 저자Hye-Sung Kim¹, Young-Youn Kim¹, Jeong-Kyu Oh¹, Kwang-Hak Bae¹*
¹Oral Health Science Research Center, Apple tree Dental Hospital, Goyang-si, Gyounggi-do, Korea
*Corresponding author● 논문요약
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to determine whether the lower intakes of yogurt, milk, and calcium are associated with periodontitis in a nationally representative sample of Korean adults.This study comprised 6,150 adults 19or more years old who took both periodontal examination and nutrition survey. The frequency of yogurt and milk intake was examined with a food frequency questionnaire. The amount of calcium intake was calculated with dietary intakes data gained from complete one-day 24-hour recall interviews. Periodontitis was assessed using the Community Periodontal Index (CPI). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed for the whole sample and subgroups with the strata of age, gender, or smoking, in a complex sampling design .Less intake of yogurt was significantly associated with periodontitis (oddsratio[OR]0.82, 95% confidential interval[CI]0.70-0.97), but neither less intake of milk (OR1.04, 95% CI 0.89-1.20)nor lower intake of calcium (OR1.04, 95% CI0.89-1.21) was significantly associated with periodontitis. In the subgroup analysis, no difference in the association of yogurt intake with periodontitis was found according to the strata of age, gender, and smoking. In conclusion, periodontitis was significantly associated with the less intake of yogurt among the Korean adults, but the calcium contained in yogurt is not likely to cause it.